Used by the struct image (image::type). More...
Macros | |
| #define | IMAGE_GREY (0) |
8 Bit Values per Pixel (0-255), One Channel (st). | |
| #define | IMAGE_BAYER (1) |
8 Bit Values per Pixel (0-255), One Channel (st), Patterned (RGRG..GBGB..RGRG...). | |
| #define | IMAGE_RGB (2) |
8 Bit Values per Pixel (0-255), Three Channels (st: R, ccmp1: G, ccmp2: B). | |
| #define | IMAGE_CBCR444 (3) |
8 Bit Values per Pixel (0-255), Three Channels (st: Y, ccmp1: U, ccmp2: V). | |
| #define | IMAGE_CBCR411 (4) |
8 Bit Values per Pixel (0-255), Three Channels (st: Y, ccmp1: U, ccmp2: V); U and V Channels have dx, dy and pitch divided by 2, which means that each 2×2 Y pixel block share the same U and V pixel. | |
| #define | IMAGE_YUVNORM (5) |
8 Bit Values per Pixel (0-255), Three Channels (st: Y, ccmp1: U*, ccmp2: V*). | |
| #define | IMAGE_IHS (6) |
8 Bit Values per Pixel (0-255), Three Channels (st: I, ccmp1: H, ccmp2: S). | |
| #define | IMAGE_RGBO (7) |
| Only used Internally. | |
| #define | IMAGE_VECTOR (8) |
8 Bit Values per Pixel (0-255), Two Channels (st: Magnitude, ccmp1: Direction (f. ex. gradient_2x2())). | |
| #define | IMAGE_GREY16 (9) |
16 Bit Values per Pixel (0-65535), One Channel (st: Always cast to (U16*)). | |
| #define | IMAGE_GREY32 (10) |
32 Bit Values per Pixel (0-232), One Channel (st: Always cast to (U32*)). | |
| #define | IMAGE_CMPLX16 (11) |
16 Bit Values per Pixel (0-65535), Two Interleaving Channels (st: [Real1, Imaginary1, Real2, ...]; Always cast to (I16*)), See vc_fft(). | |
| #define | IMAGE_CBCR422 (13) |
8 Bit Values per Pixel (0-255), Three Channels (st: Y, ccmp1: U, ccmp2: V); U and V Channels have dx and pitch (not dy) divided by 2, which means that each two Y pixel in a row share the same U and V pixel. | |
| #define | IMAGE_YCBYCR (14) |
| Only used Internally. | |
| #define | IMAGE_UNSET (0xFFFF) |
| Unset/Unused Information. | |
The type of the image defines the location and availability of data accessible over the three address pointers, st, ccmp1 and ccmp2. ccmp1 and ccmp2 are the start addresses of the additional color components. The following table gives an overview of the various image types and color components.
type | Definition | Image Type | Memory Requirement | st | ccmp1 | ccmp2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | IMAGE_GREY | Grey-Scale Image (U8) | 1 * dy * pitch | grey | — | — |
| 1 | IMAGE_BAYER | Bayer Pattern | 1 * dy * pitch | bayer | — | — |
| 2 | IMAGE_RGB | Color Image RGB | 3 * dy * pitch | red | green | blue |
| 3 | IMAGE_CBCR444 | Color Image YCbCr 4:4:4 | 3 * dy * pitch | y | u | v |
| 4 | IMAGE_CBCR411 | Color Image YCbCr 4:1:1 | 3/2 * dy * pitch | y | u | v |
| 5 | IMAGE_YUVNORM | Normalized YcbCr 4:4:4 | 3 * dy * pitch | y | u* | v* |
| 6 | IMAGE_IHS | Color Image IHS (HSI) | 3 * dy * pitch | i | h | s |
| 7 | IMAGE_RGBO | Reserved | — | — | — | — |
| 8 | IMAGE_VECTOR | Vector Image | 2 * dy * pitch | mag | dir | — |
| 9 | IMAGE_GREY16 | Grey-Scale Image (U16) | 2 * dy * pitch | grey | — | — |
| 10 | IMAGE_GREY32 | Grey-Scale Image (U32) | 4 * dy * pitch | grey | — | — |
| 11 | IMAGE_CMPLX16 | Complex Valued Image | 4 * dy * pitch | cmplx | — | — |
| 13 | IMAGE_CBCR422 | Color Image YCbCr 4:2:2 | 2 * dy * pitch | y | u | v |
| 14 | IMAGE_YCBYCR | Reserved | — | — | — | — |
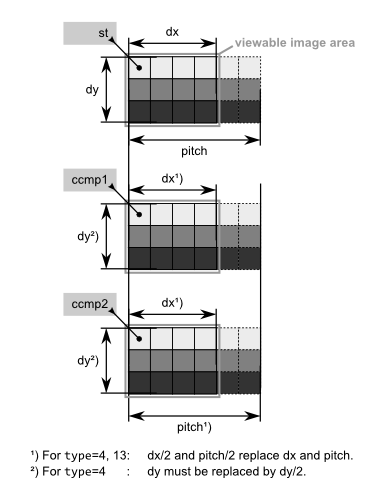
For a grey scale image, the upper left pixel is stored at address st. Going 1 to the right (x-direction), 1 must be added to this address. Going down (y-direction), pitch must be added. For a color image, two additional memory blocks are needed to store the color information. It makes sense to store these 2 blocks tightly behind the first block and behind each other, but this is not mandatory.