Data Structures | |
| struct | point |
| 2D Coordinate Point or Vector. More... | |
| struct | vcline |
| 2D Line (Normal Form). More... | |
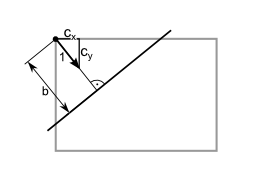
The basic data structures for geometric processing are point and vcline. The vcline uses the so-called standard form 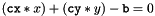 . For lines the normal vector (
. For lines the normal vector (cx, cy) should be normalized to 1, although the vcline-struct still defines a line if this is not the case: b cannot be used as the distance from the origin to the line and some trigonometric functions could have some problems. Please be aware, that even in the case of a normalized vector, the representation is not unique, since all values could be replaced by their negative, describing the very same line. All functions in this chapter use floating-point values and floating-point calculations.
Angles
There are different definitions for angles in VCLIB:
(1) Angles in radiants (rad). These are mostly used for the mathematical functions using sin() and cos(). Please note that an increasing value for a radiant angle corresponds to a CLOCKWISE rotation. The reason for this deviation from mathematical standards is the fact that the y-vector of the coordinate system points downward.
(2) Angles in degrees (deg)
(3) Angles in U8 notation (ang8) ranging from [0..255] with a resolution of approx. 1.4 degrees.
(4) Angles in U16 notation (ang16) ranging from [0..65535] with a resolution of 0.0055 degrees. This is a variant of (3) and is mainly used for angles in Hough Transform related functions to increase the accuracy.

| struct point |